Overview
Open-heart surgery is a crucial procedure for treating various heart conditions, but it often comes with significant post-operative challenges. One of the most common issues is lung complications, which affect up to 30% of patients. These complications can include fluid buildup, pneumonia, and breathing difficulties, which can slow down recovery and prolong hospital stays. Understanding these potential lung problems is vital for effective management and quicker recovery.
Dr. Shweta Bansal, a renowned pulmonologist based in Gurgaon, explains,
"It's common for patients to experience lung problems post-surgery due to prolonged intubation and reduced mobility. Typical symptoms include mild breathing difficulties and some fluid accumulation, but severe symptoms like persistent shortness of breath, high fever, or sharp chest pain require immediate medical attention."
If you are facing lung complications after heart surgery, it's important not to ignore these issues. Consult with the best pulmonologists for personalized care. Early intervention can significantly improve recovery outcomes and overall health.
Types of lung problems after heart surgery and their complication
Several types of lung problems can occur after open-heart surgery, including:
| Pneumonia |
|
| Pulmonary edema |
|
| Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) |
|
| Pulmonary embolism |
|
How Does Open-Heart Surgery Affect Your Lungs?
Open-heart surgery can affect your lungs in several ways:
- Surgical Trauma: The surgery itself can cause inflammation and fluid buildup in your lungs.
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia used during surgery can temporarily reduce lung function.
- Reduced Mobility: After surgery, staying still for too long can cause your lungs to not expand fully, leading to problems like a collapsed lung.
Intubation and Mechanical Ventilation
- Intubation: A tube is placed in your airway during surgery to help you breathe. This can irritate your lungs and increase the risk of infection.
- Mechanical Ventilation: Being on a breathing machine for a long time can lead to lung infections and tissue damage.
Knowing these factors helps in preventing and managing lung problems after surgery. Proper care and monitoring are key to a good recovery.
Lungs Recovery Time After Open-Heart Surgery
Typical Recovery Timeline
- First Week: Recovery in the hospital with close monitoring and breathing exercises.
- First Month: Gradual improvement in lung function with continued exercises.
- Three to Six Months: Most patients achieve full lung recovery within this period.
Factors Affecting Recovery Speed
- Health Conditions: Conditions like COPD or asthma can slow recovery.
- Age: Older patients may take longer to recover.
- Lifestyle: Smoking history and fitness level impact recovery speed.
- Post-operative Care: Following breathing exercises and therapy is crucial.
- Surgery Complications: Any issues during surgery can extend recovery time.
Understanding these factors helps ensure better care and a smoother recovery.
In What Cases Do Lung Problems Persist in Heart Surgery Patients?

Lingering lung problems can trouble heart surgery patients if the root cause isn't properly addressed. Without the right antibiotics, it can worsen, causing ongoing lung issues.
Several factors contribute to persistent problems:
- Surgery-Induced Lung Damage: The procedure itself may harm the lungs, creating scar tissue or fluid buildup. If untreated, these issues can lead to persistent respiratory problems, potentially requiring a lung transplant.
- Chronic Medical Conditions: Existing conditions like asthma or COPD make lung recovery tougher post-heart surgery.
- Ventilator Complications: The use of a mechanical ventilator can irritate airways, causing inflammation and ongoing respiratory problems.
- Medication Side Effects: Some medications can trigger respiratory issues, requiring treatment like inflammation reduction, oxygen therapy, or respiratory therapy. Severe cases might need hospital admission. Stay informed for a smoother recovery journey.
Do Fluids Collect in the Lungs After Open-Heart Surgery?
After open-heart surgery, it's normal for fluid to gather in the lungs, a condition called pleural effusion. This happens more often in specific groups like women or those with heart or vascular issues.
Pleural effusion can make breathing difficult and might need medical help to remove the extra fluid. For those recovering from heart surgery, close monitoring is crucial for spotting any breathing issues or signs of fluid build-up in the lungs.
Stay informed and safeguard your well-being! Explore the risks of lung problems after open-heart surgery and empower yourself for a healthier recovery.
Consult with a cardiologist and read on to learn more.
What Are the Risks of Lung Problems After Open-Heart Surgery?

The risks of lung problems after open-heart surgery include:
- Pleural Effusion: Accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity around the lungs, which can impair breathing.
- Atelectasis: Partial collapse of the lung tissue, leading to decreased oxygenation.
- Pneumonia: Increased risk due to reduced lung function and immobility during recovery.
- Pulmonary Edema: Fluid accumulation in the lung tissue, affecting gas exchange.
- Collapsed Lung (Pneumothorax): Rare but serious, requiring immediate medical attention.
These complications necessitate close monitoring and prompt treatment to manage symptoms and support lung function.
Stay proactive about your lung health! Schedule a consultation with a pulmonologist today to ensure you're on the right track for a smooth recovery.
Diagnosis and Monitoring of Lung Problems
Chest X-rays
- Purpose: To see any lung issues like fluid buildup or infection.
- Procedure: A quick and painless scan that shows images of your lungs.
CT Scans
- Purpose: To get detailed pictures of your lungs and chest.
- Procedure: A more in-depth scan that provides detailed cross-sectional images.
Pulmonary Function Tests
- Purpose: To check how well your lungs are working.
- Procedure: Breathing into a device to measure lung capacity and airflow.
Continuous Monitoring Techniques
- Purpose: To keep a constant watch on your breathing and oxygen levels.
- Procedure: Using devices like pulse oximeters to monitor oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in your blood.
Treatment for Lung Issues After Open-Heart Surgery
According to pulmonologists, lung problems are common complications after open-heart surgery. The treatment of lung problems after open-heart surgery depends on the type and severity of the problem.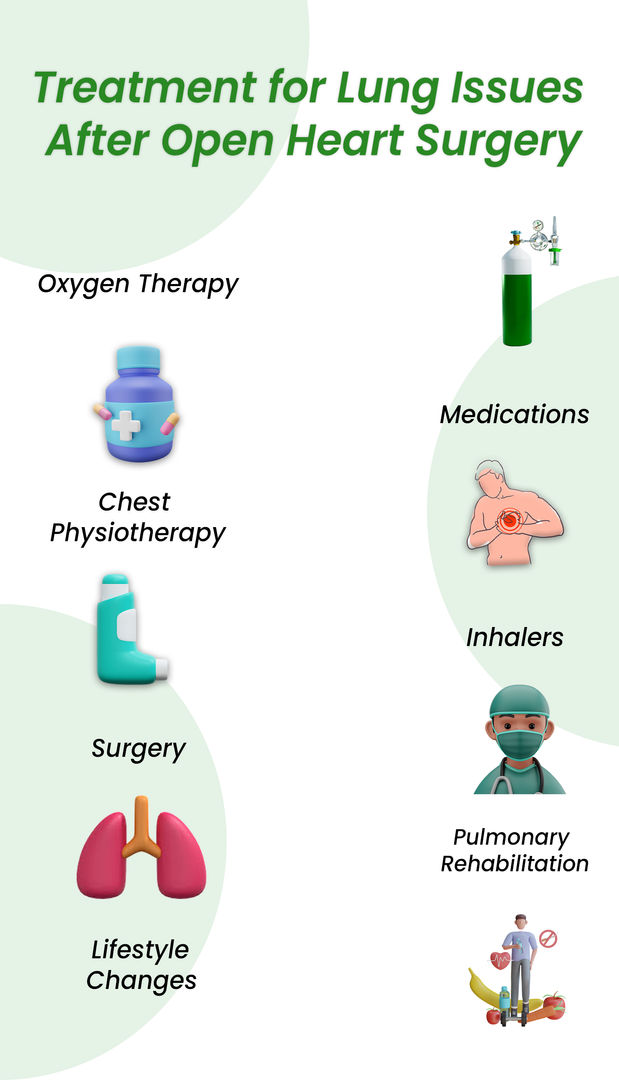
The treatment for lung issues after open-heart surgery typically involves a combination of medical management and supportive care:
- Drainage of Fluid: For conditions like pleural effusion, a procedure called thoracentesis may be performed to remove excess fluid from around the lungs.
- Respiratory Support: This can include oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation, if necessary, to aid in breathing.
- Physiotherapy: Respiratory physiotherapy is often recommended to improve lung function and facilitate the clearance of secretions.
- Medication: Antibiotics may be used to treat or prevent infections like pneumonia, and diuretics can be administered to reduce fluid overload.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular monitoring of lung function and follow-up care are crucial to detect and address any complications promptly.
Are you the one who prefers natural ways to treat your body?
Then there are some preventive measures for you!
Exercises to Cure or Prevent the Lung Problems
To boost lung function and prevent issues post-open-heart surgery, concentrate on simple breathing exercises and gradual physical activity. Some effective exercises include:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: These involve taking slow, deep breaths to expand the lungs fully. They help in improving lung capacity and preventing atelectasis.
- Incentive Spirometry: This uses a device to encourage deep breathing, which can prevent lung complications post-surgery.
- Coughing Exercises: Gentle coughing helps clear mucus from the lungs, which is crucial for preventing infections.
- Walking: Gradually increasing walking distances helps enhance cardiovascular health and lung function.
- Arm and Leg Movements: Gentle movements of arms and legs can improve blood circulation and overall fitness.
- Chair Exercises: For those with limited mobility, exercises that can be done while sitting in a chair can be beneficial.
Please Note: It is important to consult with the experts before starting any new exercise program, especially after open-heart surgery. Your healthcare provider can help you determine the best exercises for your specific needs and provide guidance on proper technique and intensity. his may include taking prescribed medications as directed, getting enough rest, and avoiding strenuous activities until your healthcare provider advises otherwise.
Conclusion
Understanding lung complications after open-heart surgery is crucial for a successful recovery. Key points include the common types of lung problems such as pneumonia, atelectasis, pleural effusion, ARDS, and pulmonary edema, and the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Factors like pre-existing conditions, age, lifestyle, post-operative care, and surgical complications can affect lung recovery time.
Proactive post-surgery care, including regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider, adherence to prescribed breathing exercises, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can significantly improve your recovery outcomes.
FAQs
What are the most common lung complications after open-heart surgery?
- Pneumonia, atelectasis, pleural effusion, ARDS, and pulmonary edema are the most common lung complications.
How can I reduce the risk of lung complications post-surgery?
- Follow your doctor’s instructions, perform breathing exercises, stay mobile, and avoid smoking.
How long does it take for lung function to return to normal after surgery?
- Most patients see significant improvement within the first month, with full recovery typically within three to six months.
What should I do if I experience shortness of breath after surgery?
- Contact your healthcare provider immediately, as this could be a sign of a serious complication.
Can pre-existing lung conditions affect recovery?
- Yes, conditions like COPD or asthma can slow down recovery and may require additional management.
References:
https://healthblog.uofmhealth.org/