Introduction
Eczema, also referred to as atopic dermatitis, is one of those daily skin issues that millions of people live with. The perpetual itching, flare-ups, red spots, and pain can make life quite frustrating. Although there are a variety of eczema ointments, eczema treatment creams, and various types of medicine for dermatitis, not everyone enjoys long-term relief. Some people deal with severe eczema that doesn’t respond well to standard therapies. Over the last decade, Stem Cell Research has opened new doors for conditions that were once thought to be untreatable, and eczema is now one of them.
Stem treatment, especially mesenchymal stem cell therapy, is showing promising results in reducing inflammation, calming atopic skin, and even repairing the skin barrier. This blog dives deep into the causes of eczema, why current methods often fall short, and how stem cell therapy could be the future of atopic dermatitis treatment. We’ll also look at benefits, risks, cost factors like stem cell storage cost and stem cell preservation cost, and the bigger picture of where research is heading. Connect with the best medical professional to learn in-depth about stem cell treatment for Eczema.
What Is Eczema?
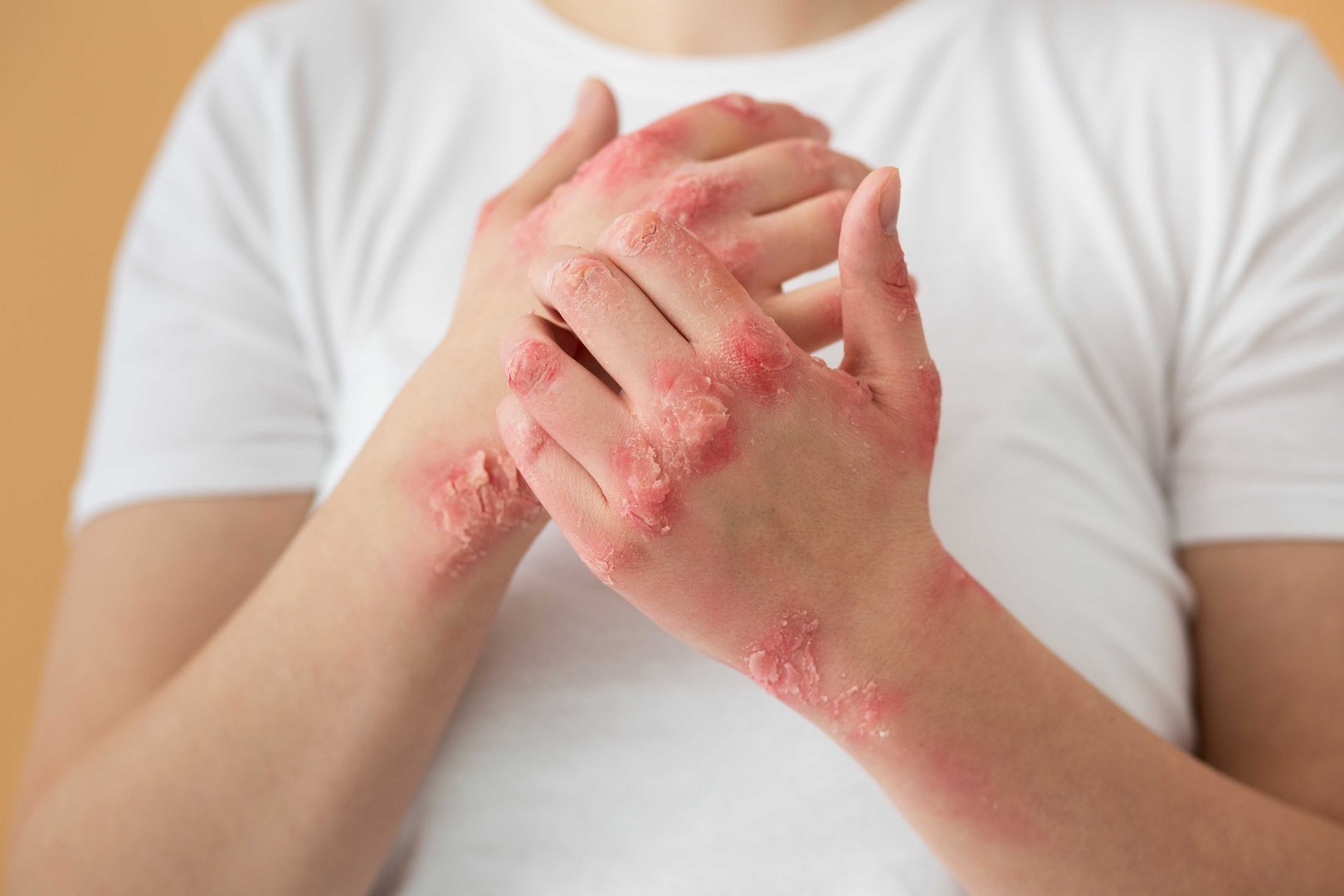
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is an immune-mediated skin disease that occurs in both children and adults. It's not just a case of eczema rash treatment—it's an ongoing immune system disorder. The skin will be inflamed, itchy, red, and extremely sensitive. Eczema can develop on any part of the body, from the face to arms and legs, and in some individuals, it spreads extensively over the body.
The precise eczema reasons are not entirely known, but studies indicate it usually originates from an overactive immune system response to common exposures such as dust, pollen, soaps, or even stress. Genes play a part, too—if a parent has atopic skin or allergies, the child is more likely to have eczema. Atopic dermatitis signs and symptoms are recurrent itching, swelling, dry skin, and occasionally infections due to relentless scratching. Curiously, it is not just humans that are afflicted; there's also canine atopic dermatitis in dogs, which appears and acts very much like what happens in humans.
Physicians typically diagnose eczema by examining atopic dermatitis symptoms and looking up the patient history. But for all the advances in dermatology, the root problem—a T-cell immune imbalance—remains difficult to fully manage with traditional measures.
Current Standard Treatment For Eczema
When you see a physician for treatment of eczema, the initial treatment tends to include creams or an eczema ointment. Corticosteroids, antihistamines, and immunosuppressants are common drugs prescribed. For mild eczema, an eczema treatment cream with moisturizers will heal the skin barrier. For more severe eczema or moderate eczema, physicians may prescribe more powerful medicines for eczema, including biologics such as dupilumab, or systemic medicine for dermatitis that inhibits the immune response.
Still, these solutions are not perfect. Patients often need lifelong use, and over time, the body may stop responding to the medicine for eczema. Some drugs come with side effects like thinning of the skin, infections, or other health risks. People with atopic dermatitis often try several options before finding a balance, but for many, flare-ups return. This is why researchers in clinical research studies and the immunology journal are now advocating for new methods, which leads us to stem transplant and T cell therapy.
Why Consider Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy is investigated because it is more than a surface-level treatment for eczema rashes. Rather than only soothing the itching or redness temporarily, stem treatment addresses the issue at its source by restoring balance to the immune system and mending the compromised skin structure. In clinical trials, mesenchymal stem cells therapy has been proven to modulate T cell function, which is one of the key forces behind symptoms of atopic dermatitis. T cells are part of our body's immune system that usually keep the body safe, but in eczema, they become hyperactive and trigger inflammation. Through the application of T cell treatment or T cell therapy with stem cells, scientists hope to reboot this immune discrepancy. This is particularly critical for patients suffering from severe eczema who have tried nearly every dermatitis medicine known to man. One of the reasons stem cell therapy is so exciting is due to its regenerative ability. Stem cells from the umbilical cord, for example, can not only suppress inflammation, but also repair skin tissue, so the skin becomes less likely to suffer constant irritation. And that is why Stem Cell Research is being comprehensively funded in this field, and each additional clinical trial brings with it more hope. If you are considering stem cell therapy as a viable treatment option, book an online doctor consultation on our platform in just minutes.

Types Of Stem Cells Used
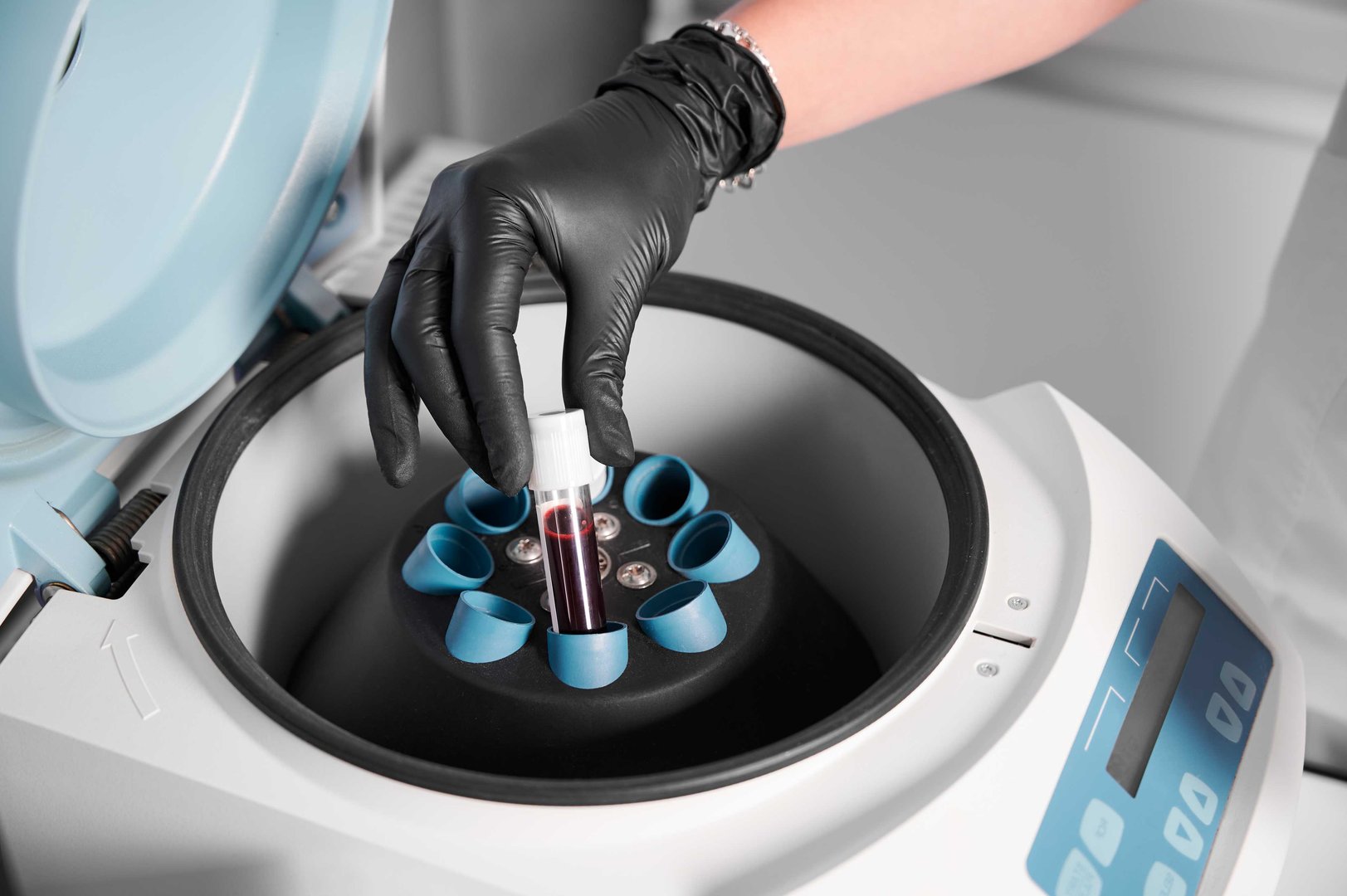
Various forms of stem cells are being researched for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. The most prevalent in ongoing clinical trials are mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are traditionally harvested from bone marrow, fat tissue, or the umbilical cord. MSCs are the most favored because they are safe, versatile, and can be employed in either stem transplant or stem cell donation procedures. Umbilical cord stem cells are becoming very popular due to the fact that they are young, healthy, and do not cause as much immune rejection as other varieties. Stem cell storage and stem cell preservation are questions that are frequently raised by patients, and this is where cord blood banking comes in. Through the storage of umbilical cord tissue after birth, families are able to make stem cells available for therapies such as eczema treatment or even other ailments in the future. Though stem cell storage price and stem cell preservation price differ from nation to nation, families view it as a health investment of the long term. Additional cell-based therapies, such as T cell therapy, are also under investigation. In certain research, genetically engineered T cells or immune cell therapies are combined with stem cells to modulate immune overreaction in atopic skin.
Benefits Of Stem Cell Therapy
The advantages of stem cell therapy for eczema are becoming more evident with each new influx of clinical trial data. Individuals with severe eczema who were not treated with eczema ointment or eczema medicine exhibited considerable improvement after mesenchymal stem cell therapy. Some of the key advantages are:
- Decrease in itching, redness, and eczema rash treatment requirements.
- Repair of the skin barrier, which renders atopic skin less sensitive.
- Equilibrating of T cells, lowering chronic inflammation.
- Potential lowering of the use of corticosteroids and other aggressive medicines for dermatitis.
- Long-term outcomes as opposed to short-term relief from eczema treatment cream.
For individuals who have wrestled with eczema treatment for decades, these advantages can represent a new way of life. Atopic dermatitis-affected families with children also have hope in these treatments, as persistent scratching in children can cause infections and sleep disorders. Even in the animal kingdom, research on canine atopic dermatitis is now looking into stem treatment as a possibility. One will get the best results from stem cell therapy if treatment is taken from doctors in India.
Risks & Limitations Of Treatment
As with any new medical treatment, stem cell therapy has its risks and limitations. Clinical trials are ongoing, and although initial results are encouraging, it is not a panacea yet. Some of the risks are immune rejection (rare with mesenchymal stem cell therapy), infections following stem transplant, and expense. A further limitation is availability.
Not all hospitals or clinics provide stem treatment, and most programs are still within a clinical trial environment rather than a part of traditional healthcare. Approvals depend on the country, and insurance does not usually pay for such experimental medicine for eczema. There's also the issue of ethics regarding stem cell donation and use, but the use of umbilical cord cells is generally viewed as less controversial. It's also important to mention that not all patients react similarly. Some get significant improvement, whereas others notice minimal variations in their atopic eczema.
Who Can Be An Ideal Candidate?
Not all persons who have atopic dermatitis symptoms require stem treatment. Suitable candidates are typically those suffering from severe eczema that won't respond to standard medicine for dermatitis, biologics, or eczema treatment cream. Adults and kids with chronic atopic eczema who experience recurrent flare-ups in spite of routine eczema rash treatment may be eligible. Individuals with autoimmune imbalances, or those in whom T cells are extremely overactive, are also candidates for T cell therapy with the use of stem cells. But doctors typically suggest enrolling in a clinical trial first to have adequate monitoring and safety. For canine atopic dermatitis, veterinary scientists are also enrolling dogs having chronic diseases that have not responded to conventional medicine. One should ask detailed questions to the doctor before considering stem cell therapy as a treatment option.

Cost & Accessibility Of Treatment
One of the major apprehensions of patients thinking of stem cell treatment for eczema is its price tag. Stem cell preservation price and stem cell storage price are already substantial for families opting for cord blood banking. The treatment procedure itself, particularly if it is in the form of a stem transplant or high-end T-cell treatment, can be extremely costly. In nations such as the US or Europe, the price can be tens of thousands of dollars based on the clinic, the type of stem cell, and the number of sessions needed. Availability is also a problem—this therapy is available only from specialized centers or clinical research trial hospitals. In third-world nations, the therapy is still uncommon, and most individuals seek it abroad. Having said that, with Stem Cell Research improving and more clinical trial outcomes being published in immunology journals, the cost should eventually come down and accessibility increase.
Future Scope Of Treatment
The future of stem cell therapy for atopic dermatitis is quite bright. Researchers are not just exploring mesenchymal stem cell therapy but also integrating it with T cell therapy, gene modification, and biomaterials to enhance skin repair. Canine atopic dermatitis clinical trials are also providing important information that could be utilized for human use. The fact that stem treatment addresses both eczema causes and symptoms gives it a strong edge over current medicine for eczema. With continued funding in Stem Cell Research, more advanced clinical trials, and better stem cell preservation methods, the therapy could become mainstream in the next decade. For now, patients with severe eczema can look toward this as a future possibility, especially if standard treatment for eczema keeps failing.
Summary
Eczema or atopic dermatitis remains a condition that plagues millions of people across the globe, with cases of atopic skin issues varying from mild eczema rash treatment requirements to full-blown eczema that is resistant to all medication for dermatitis. Present choices, such as eczema ointment or eczema treatment cream, can temporarily cure, but hardly address the underlying immune imbalance created by T cells.
Stem cell therapy, particularly mesenchymal stem cell therapy from umbilical cord sources, is a new avenue that soothes inflammation, regenerates skin, and modulates immune responses. Clinical trial outcomes are encouraging, yet risks, expense, and accessibility issues continue to restrict universal application. Stem cell storage, stem cell preservation, and the costs involved remain practical hurdles for most families. Nevertheless, as Stem Cell Research continues and additional immunology journal reports substantiate its advantages, stem treatment could revolutionize the eczema treatment and atopic dermatitis therapy of the future, not only for humans but even canine atopic dermatitis. The quest continues, but hope is now brighter than ever.