Overview:
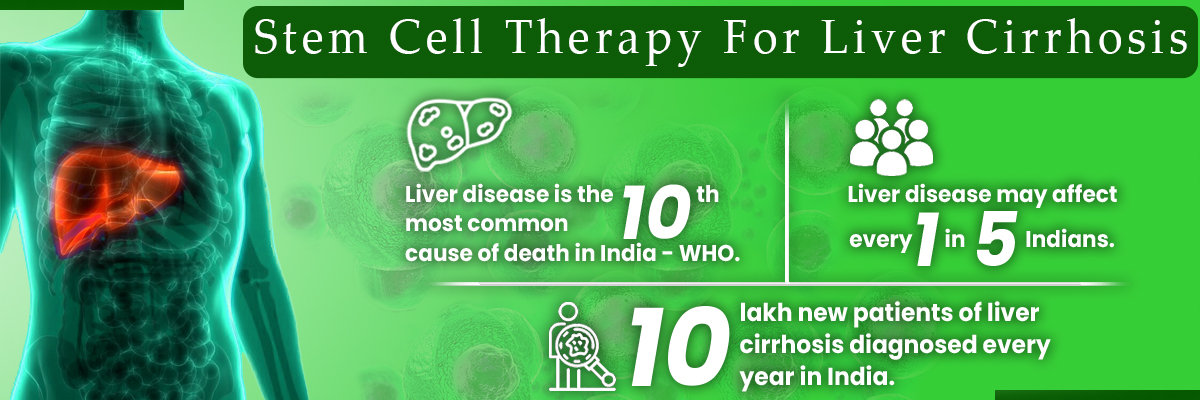
Autoimmune diseases are a growing health concern in India, impacting millions. These conditions occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, causing chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and long-term health issues. Recent studies suggest that over 10% of India’s population is affected by autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis (MS), type 1 diabetes, and Crohn’s disease.
With limited success from conventional treatments, stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases is emerging as a cutting-edge, natural alternative that targets the root cause—immune system dysfunction. This article explores how stem cells work in autoimmune conditions, FDA approval status, treatment procedures, costs in India, and the advantages of regenerative healing.
Ready to Take Control of Your Autoimmune Condition?Contact us today to begin your journey toward long-term relief and immune system restoration, or you can alos book online doctor consultation in just few clicks.
Types of Autoimmune Diseases Treated with Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is emerging as a groundbreaking treatment option for various autoimmune diseases. These conditions occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues. Traditional treatments often focus on symptom management, but stem cell therapy aims to reset and rebuild the immune system, offering the potential for long-term relief and improved quality of life.
Below are some of the most common autoimmune diseases where stem cell therapy has shown promising results:
1. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the joints.
Stem cell therapy for RA works by:
- Reducing joint inflammation and pain.
- Modulating the immune system to prevent further damage.
2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs including the skin, kidneys, and joints.
Stem cell therapy for lupus helps:
- Suppress autoimmune attacks.
- Halt disease progression.
- Repair damaged tissues at a cellular level.
3. Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple Sclerosis is a neurological disorder where the immune system attacks the protective covering of nerves.
Stem cell therapy for MS is designed to:
- Reset the immune system.
- Promote repair of the nervous system.
- Reduce relapses and improve motor function.
4. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Stem cell treatment for diabetes aims to:
- Regenerate insulin-producing cells.
- Reduce or eliminate insulin dependence.
- Improve blood sugar control and metabolic function.
5. Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes chronic inflammation of the digestive tract.
Stem cell therapy for Crohn’s disease works by:
- Modulating immune responses in the gut.
- Promoting healing of damaged intestinal tissues.
- Reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
How Does Stem Cell Therapy Work for Autoimmune Conditions?
Stem cells are unique cells with the ability to self-renew and differentiate into various specialized cell types. In the context of autoimmune diseases, stem cell therapy works by “rebooting” the immune system, enabling the body to stop attacking itself and begin healing.
Key mechanisms include:
- Reprogramming faulty immune cells to function correctly.
- Restoring immune tolerance, preventing the immune system from attacking the body’s own tissues.
Types of Stem Cell Transplants Used
. 1. Autologous Stem Cell Transplant (ASCT)
- Involves using the patient’s own stem cells.
- Stem cells are then reintroduced to regenerate a healthier immune system.
2. Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant
- Uses stem cells from a healthy donor.
- More suitable for severe or treatment-resistant autoimmune conditions.
- Offers the advantage of introducing a completely new immune system.
- Requires careful matching and monitoring to prevent rejection or GVHD.
Stem Cell Transplantation Procedure
The stem cell therapy process for autoimmune diseases involves several critical steps:
1. Pre-transplant Evaluation
- Comprehensive medical testing and imaging to assess eligibility.
- Includes blood tests, organ function tests, and immunological assessments.
2. Stem Cell Harvesting
3. Conditioning Regimen
- Patients undergo a conditioning phase with high-dose chemotherapy or immunosuppressive drugs.
- This eliminates the malfunctioning immune cells responsible for the autoimmune attacks.
4. Stem Cell Infusion
- Collected stem cells are infused into the patient’s bloodstream.
- They migrate to the bone marrow and begin to regenerate a new immune system.
5. Post-transplant Monitoring
- Continuous monitoring for signs of recovery, infection, or complications.
- Regular follow-ups to track immune function, inflammation levels, and organ health.
Take the First Step Toward Immune Reset and Healing - Schedule your consultation today to learn how regenerative stem cell therapy can support long-term healing and immune balance.

Is stem cell therapy FDA Approved for autoimmune diseases?
Currently, stem cell therapy is not FDA-approved for autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, or Crohn’s disease. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has only approved stem cell treatments for certain blood-related conditions, like leukemia and lymphoma (hematopoietic stem cell transplants).
However, the landscape is evolving. There are numerous ongoing clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases.
Conditions such as:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- Crohn’s Disease
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
While not yet FDA-approved in the U.S. for autoimmune indications, stem cell therapy is legally offered in other countries like India through accredited regenerative medicine clinics.
How Much Does Stem Cell Therapy Cost for Autoimmune Disease?
One of the major advantages of choosing India for regenerative treatment is the affordability and high-quality care. The cost of stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases in India ranges between USD $8,000 to $12,000, depending on several factors:
Factors Influencing Cost:
- Type of Autoimmune Disease (RA, MS, SLE, etc.)
- Type of Stem Cells Used (Autologous vs. Allogeneic)
- Source of Stem Cells (Bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord, etc.)
- Hospital or Clinic Location
- Customization of Treatment Plan
- Pre-treatment Evaluations and Post-care Monitoring
By comparison, the same stem cell procedure in the United States can cost anywhere from USD $25,000 to $50,000, making India a cost-effective alternative with no compromise on safety or technology.
Discover your personalized stem cell therapy options and get detailed cost insights—visit ClinicSpots to take the next step toward advanced autoimmune disease treatment in India.
Advantages of Stem Cells for Autoimmune Diseases
Stem cell therapy offers various advantages:
- Resets the Immune System
Targets the root cause, not just the symptoms. - Offers Long-Term Relief
Potential for sustained remission and fewer flare-ups. - Modifies Disease Progression
Acts at the cellular level to control immune dysfunction. - Personalized & Targeted
Customized treatment based on the specific autoimmune condition.
Advantages of Stem Cells for Autoimmune Diseases Over Traditional Treatments
Stem cell therapy offers long-term remission, immune system reset, fewer side effects, and reduced drug dependency—unlike traditional treatments that only manage autoimmune symptoms.
Aspect | Traditional Treatments | Stem Cell Therapy |
Treatment Focus | Manages symptoms | Resets immune system and targets root cause |
Medication Use | Lifelong immunosuppressants | Reduced or no long-term drug dependency |
Long-Term Results | Temporary relief, frequent flare-ups | Potential for long-term remission |
Side Effects | Risk of organ damage, hormonal imbalance | Temporary immune suppression, fewer long-term risks |
Disease Modification | Does not change disease progression | Alters immune response at cellular level |
Personalization | One-size-fits-all approach | Customized, condition-specific treatment plans |
Who is Eligible for Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases?
Stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases is an advanced treatment option, but not every patient qualifies. Here are the key eligibility criteria:
- Confirmed Autoimmune Diagnosis: A clear medical diagnosis of an autoimmune disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, or Crohn’s disease is essential.
- Severe or Treatment-Resistant Disease: Ideal for patients with aggressive progression or those who do not respond to conventional treatments.
- Good General Health: Candidates must not have severe heart, kidney, or liver conditions to tolerate stem cell transplantation.
- Age Considerations: While there’s no strict age limit, younger patients may recover faster and with fewer complications.
- Previous Treatment History: Those who’ve exhausted standard therapies like steroids, immunosuppressants, or biologics may benefit more.
- Informed Consent: Understanding stem cell therapy risks and benefits is vital before starting the procedure.
Stem Cells for Autoimmune Diseases: Understand the Procedure, Before & After
Before the Procedure
- Comprehensive Evaluation: A detailed review of medical history, type and severity of the autoimmune condition, and prior treatments.
- Informed Consent: Patients are counseled about the procedure, risks, success rates, and alternatives.
- Stem Cell Source Selection:
- Autologous Stem Cells: Collected from the patient’s own body.
- Allogeneic Stem Cells: Sourced from a healthy, HLA-matched donor.
- Stem Cell Mobilization (Autologous): Medications are used to move stem cells from bone marrow into the bloodstream for collection.
- Stem Cell Harvesting: Cells are extracted from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or adipose (fat) tissue depending on the medical condition and treatment protocol.
During the Procedure
- Conditioning Therapy: High-dose chemotherapy or immunosuppressive drugs are administered to eliminate the faulty immune response and prepare for engraftment.
- Stem Cell Infusion: Processed and purified stem cells are infused into the patient’s bloodstream. These cells then migrate to the bone marrow, where they regenerate into healthy immune cells.
After the Procedure
- Close Monitoring & Recovery: Patients are monitored for potential side effects such as infections or graft-versus-host disease (in allogeneic cases).
- Immune System Rebuilding: Over weeks to months, the new stem cells help rebuild a healthier immune response, potentially halting disease progression.
- Long-term Follow-Up: Regular blood tests, imaging, and consultations are necessary to track therapy success and adjust medications.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Patients are encouraged to maintain a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and avoid known autoimmune triggers to support recovery.
What to Expect After Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases
Undergoing stem cell treatment for autoimmune diseases is a significant step, and understanding what comes next is crucial for a smooth recovery and successful results.
Initial Recovery Phase
- Fatigue and Weakness: It’s normal to feel tired, weak, or low-energy in the first few weeks after therapy. Your body is adjusting and beginning to rebuild a new immune system.
- Healing Time: Recovery time may vary depending on the autoimmune condition (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or multiple sclerosis) and whether autologous or allogeneic stem cells were used.
Regular Monitoring
- Frequent Check-Ups: Your doctor will closely monitor your progress with blood tests, imaging, and immune system markers.
- Therapy Response: Specialists will assess how your symptoms improve and ensure the stem cells are successfully engrafting and restoring immune balance.
Gradual Symptom Improvement
- Many patients experience a reduction in autoimmune symptoms like inflammation, pain, or fatigue within a few months.
- Response times vary, and not all patients will see immediate results. However, long-term remission is possible for many.
Potential Side Effects of Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases
Like any medical treatment, stem cell therapy for autoimmune disorders comes with potential risks. Here’s what you should know:
Common Side Effects
- Infection Risk: Due to a temporarily weakened immune system during recovery.
- Fever or Rash: These are typical immune reactions post-transplant and should be monitored closely.
- Adverse Reactions to Medications: Including nausea, fatigue, or mild allergic responses during conditioning or after the infusion.
Serious Complications
- Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD):
A risk primarily in allogeneic transplants (donor stem cells). Here, the new immune cells may attack the body. Watch for symptoms like:- Persistent skin rashes or irritation
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)
- Severe mouth dryness or ulcers
- Eye dryness or discomfort
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Fertility Issues: Some conditioning regimens may affect fertility, especially in younger patients. Discuss fertility preservation options beforehand.
Conclusion:
Stem cell therapy presents a breakthrough approach for treating autoimmune diseases by targeting the root cause—immune system dysfunction. Offering regenerative healing, reduced dependency on medications, and potential long-term remission, stem cell therapy in India combines advanced technology with affordable, personalized care. For patients suffering from conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, and Crohn’s disease, this innovative treatment offers hope for lasting relief and improved quality of life.
References:
https://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2023-05-06-autoimmune-disorders-found-affect-around-one-ten-people
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0952791522001133