Overview
Breast augmentation is a widely sought cosmetic procedure that helps women enhance breast size, restore shape after pregnancy or weight changes, and achieve better body proportion. The surgery typically involves silicone or saline implants, or in some cases fat transfer, to create natural-looking volume and contour. As demand continues to grow globally, breast augmentation remains a well-established option for women seeking improved confidence, provided it is performed by a Qualified surgeon with careful consideration of safety, risks, and individual goals.
Breast Augmentation
Most women choose breast reconstruction to feel more confident and restore their shape after pregnancy or weight changes. Others hope to balance their body proportions.
The procedure usually involves placing implants, either silicone or saline, under the breast tissue or chest muscle. In some cases, surgeons may also perform a fat transfer. As the name implies, this technique uses fat from another part of the body to add volume and shape to the breasts, creating a more natural look.
Since the breast implant industry is anticipated to reach over USD$5 billion by 2034, it shows how in-demand this surgery has become worldwide. In other words, breast augmentation is here to stay.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any cosmetic procedure, breast augmentation comes with potential risks and complications. These can include:
A thorough medical evaluation before surgery serves as a crucial safety checkpoint. That’s why it’s important to choose a skilled surgeon who works at an accredited facility if you're looking for the best breast augmentation. That's because they follow strict rules to prevent complications. Accredited centers also track results and work on improving quality. When visiting a facility, it’s best to ask about its accreditation and infection rates, as well as how it handles emergencies.
Note that a reputable surgeon will review your health history, current medications, and any chronic conditions that might affect healing.
Types of Breast Implants and Materials
As mentioned, breast augmentation can be done using different types of implants. The most common implants are silicone and saline. Let’s break them down:
Silicone Implants
Silicone breast implants use cohesive gel technology that closely mimics natural breast tissue. The filling maintains its shape rather than freely flowing if the shell breaks. They require a slightly larger incision for placement. Regular MRI scans or
Silicone breast implants use cohesive gel technology that closely mimics natural breast tissue. The filling maintains its shape rather than freely flowing if the shell breaks. They require a slightly larger incision for placement. Regular MRI scans or ultrasound check-ups are recommended to detect silent ruptures, since any leaks may not be immediately noticeable.
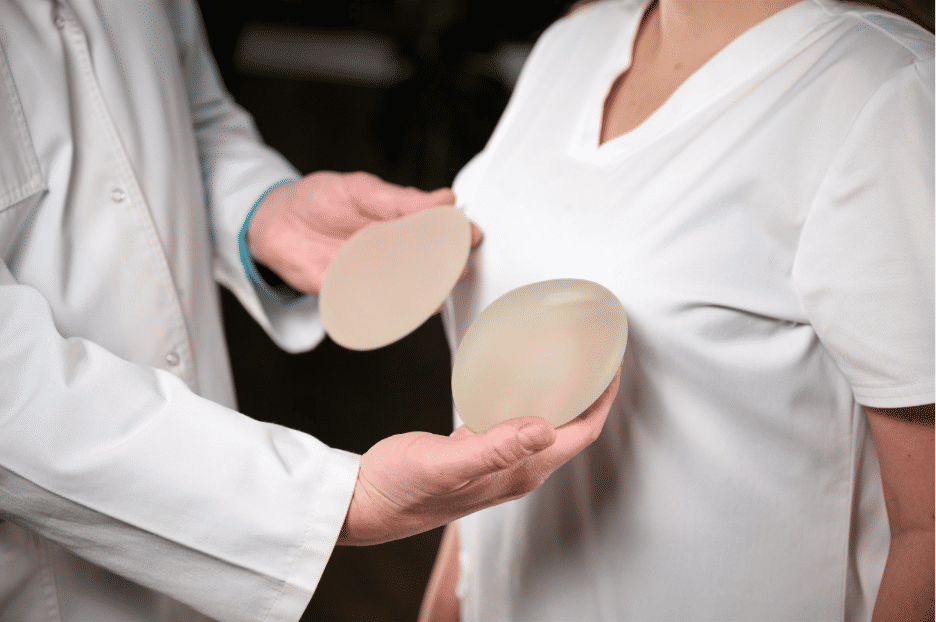

Saline Implants
Unlike cohesive silicone gel, saline implants are filled with sterile saltwater, which can be adjusted slightly during surgery for the best fit. They tend to feel firmer and may show ripples, especially in women with less natural breast tissue. If the implant ruptures, the fluid is safely absorbed by the body and the breast deflates. Another factor you may want to know is that they're usually less expensive than silicone.
Who Is a Good Candidate?
While this type of breast surgery has many benefits to offer, it is not for everyone. There are factors to consider when determining if the procedure is suitable for you. Generally, good candidates are:
- Physically healthy: Free from medical conditions that could complicate surgery or recovery.
- Non-smokers or willing to quit: Smoking can interfere with healing.
- Realistic about results: Understanding what implants or reconstruction can achieve is key.
- Done growing: Typically, candidates are over 18 for saline implants and over 22 for silicone implants.
- Seeking revision: People who have had previous breast enhancement but are unhappy with the results may also be good candidates.
- Looking for improvement, not perfection: The procedure can enhance shape and confidence. However, it won’t completely change your life or solve unrelated self-esteem issues.
Before your surgery, your surgeon will perform a thorough pre-operative health screening to ensure you are ready and fit for the procedure. This step helps reduce risks and support a safe and smooth recovery.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding With Implants
Many women undergo breast augmentation before completing their families. And this often raises questions about prenatal care or pregnancy and nursing.
Breast implants generally don't prevent successful breastfeeding, but the way the surgery is done matters. Incisions made around the areola carry a higher risk of affecting milk ducts or nipple sensation. Meanwhile, incisions placed in the breast fold or armpit are less likely to cause these issues.
Pregnancy naturally changes breast tissue, and these changes happen whether implants are present or not. The added weight and hormonal effects may increase the rate at which implants shift or sag. This can sometimes lead to earlier revision surgery. Most surgeons suggest waiting at least six months after weaning before considering any revision. This gives the breast tissue time to settle and stabilize.
Conclusion
Breast augmentation can be a life-changing procedure for many women. It helps to restore shape, improve body proportions, and boost confidence. So, when you ask if it’s safe, the short answer is yes, if you meet important criteria. Also, it's critical to work with an experienced surgeon who can guide you through the process, explain your options, and help manage potential risks. It's better to take your time, ask questions, and fully understand the procedure than to rush into a decision.